What is the “You’ve Been Hacked!” email scam
The “You’ve Been Hacked!” email is a type of extortion scam email that falsely claims the recipient’s computer has been hacked. The sender claims to have stolen all the information in the computer and threatens to reveal it if a payment of $250 is not made to the provided Bitcoin wallet address. Paying would be a waste of money because the contents of the email are false.
The “You’ve Been Hacked!” scam email will first catch users’ eye with an alarming subject line saying users’ computers have been hacked. If users open the email, they will be greeted with a message saying all of their information has been stolen. The sender claims to have stolen all login credentials (payment systems, social media, email, messengers, etc.), correspondence history (emails, messages, etc.), and all files from the computer. They threaten to sell all of the data on a darknet marketplace unless the recipient agrees to pay $250 in Bitcoin to the provided wallet address.
This email is a good example of an extortion scam. The contents are completely false but the threatening way the email is written may make users anxious enough to pay the money. Malicious actors use various scare tactics to pressure users into paying, and unfortunately, they sometimes pay off. A type of extortion, known as sextortion email scams have proven to be quite successful. Such emails threaten to publicly release users’ explicit videos unless a payment is made. The emails are often written in a very mocking and alarming way, to shame users and pressure them into paying.
These types of emails are always fake, no matter how legitimate the claims may seem. Paying would be a complete waste of money.
Here are the full contents of the “You’ve Been Hacked!” scam email:
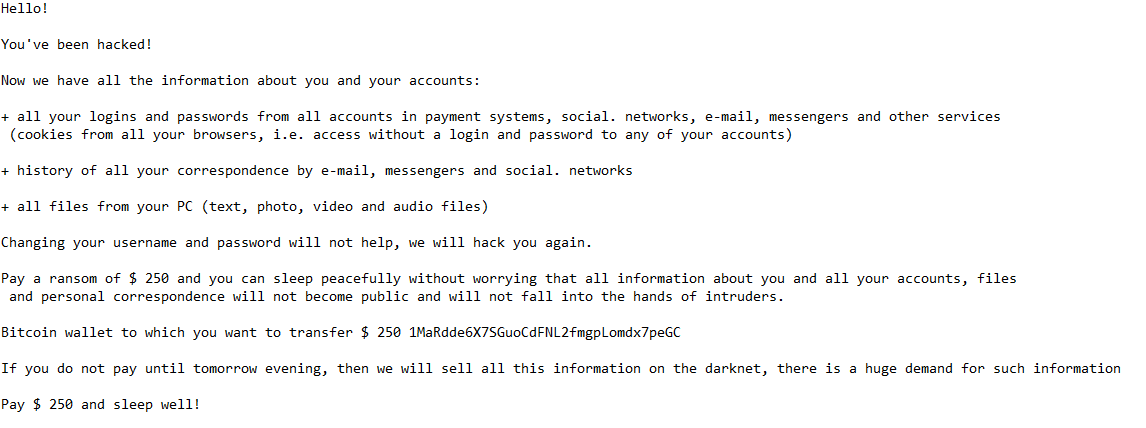
Hello!
You’ve been hacked!
Now we have all the information about you and your accounts:
+ all your logins and passwords from all accounts in payment systems, social. networks, e-mail, messengers and other services (cookies from all your browsers, i.e. access without a login and password to any of your accounts)
+ history of all your correspondence by e-mail, messengers and social. networks
+ all files from your PC (text, photo, video and audio files)
Changing your username and password will not help, we will hack you again.
Pay a ransom of $ 250 and you can sleep peacefully without worrying that all information about you and all your accounts, files and personal correspondence will not become public and will not fall into the hands of intruders.
Bitcoin wallet to which you want to transfer $ 250 1MaRdde6X7SGuoCdFNL2fmgpLomdx7peGC
If you do not pay until tomorrow evening, then we will sell all this information on the darknet, there is a huge demand for such information
Pay $ 250 and sleep well!
Why are you receiving scam emails?
These types of threatening emails always claim that users received the email because their computers have been hacked. However, in reality, users receive the emails because their email addresses have been leaked, not because their computers are infected with malware. If you received a threatening scam email, some service you used the email address to register for has either leaked the address or suffered a cyber attack. You can check whether it has been leaked and which breach your email address is part of on HaveIBeenPwned. Unfortunately, receiving this email is proof that your email address has been leaked. There’s nothing you can do once your email address has been leaked, though you can at least be on the lookout for suspicious emails in the future. You will likely receive more similar emails in the future. And not only scam emails, but you may also receive emails carrying malware. Thus, you need to be very careful with unsolicited emails.
In some cases, malicious actors operating these scam campaigns include users’ passwords. This method adds credibility to the email because in users’ minds, how else would the sender have their password if not because they hacked the computer? In reality, passwords are stolen the same way as email addresses. If you use unique passwords, you can easily guess which service leaked it. Many platforms and services have very poor security and store passwords in plain text. If they’re ever successfully targeted in a cyberattack, malicious actors would be able to steal the passwords. Stolen passwords are sold on various hacker forums for other cybercriminals to purchase.
You can check whether your password has even been leaked here. If an extortion email ever reveals a password you use, it goes without saying that you need to change it immediately for all accounts you use it for. Ideally, you should always use unique passwords for each account. Passwords should also be difficult to guess, and be made up of combinations of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Password managers are great tools for users who struggle with password creation.
Site Disclaimer
WiperSoft.com is not sponsored, affiliated, linked to or owned by malware developers or distributors that are referred to in this article. The article does NOT endorse or promote malicious programs. The intention behind it is to present useful information that will help users to detect and eliminate malware from their computer by using WiperSoft and/or the manual removal guide.
The article should only be used for educational purposes. If you follow the instructions provided in the article, you agree to be bound by this disclaimer. We do not guarantee that the article will aid you in completely removing the malware from your PC. Malicious programs are constantly developing, which is why it is not always easy or possible to clean the computer by using only the manual removal guide.