What is the “Saved Passwords Were Found Online” email scam
“Saved Passwords Were Found Online” email is a phishing attempt that tries to trick users into revealing their login credentials. The email claims that users’ passwords have been exposed and must be changed to protect accounts. If users engage with the email and follow the instructions, they will reveal highly sensitive information to cybercriminals.
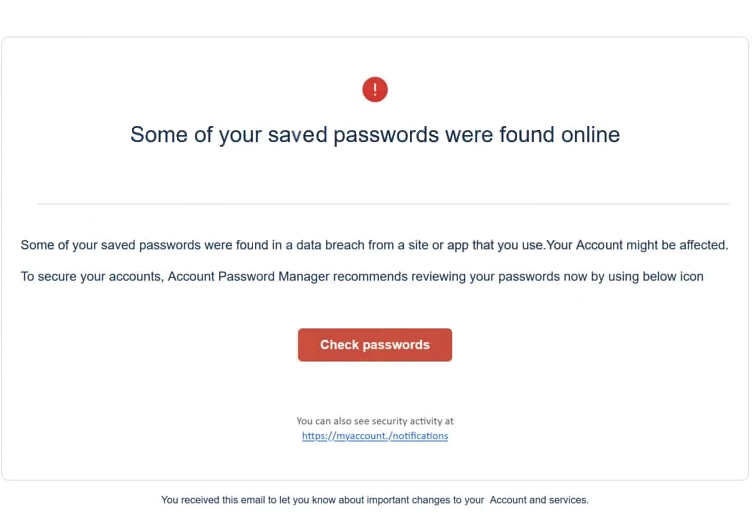
This “Saved Passwords Were Found Online” email scam is a classic phishing attempt. The email claims some of the recipient’s passwords have been exposed in a data breach of a site/app they use. The email is supposed to look like an alert from a password manager service. Specifically, the email is supposedly from a password manager called Account Password Manager.
To supposedly secure accounts, users are asked to review their passwords by clicking on the provided “Check passwords” button. If users click on the button, they will be taken to a site that’s supposed to imitate an email login page. The site asks users to type in their passwords, and if users do, the passwords will be transferred to the malicious actors operating this scam. The stolen password(s) will either end up on a hacker forum along with other users’ passwords or will be used by the malicious actors themselves. Either way, users’ email accounts would be hijacked.
The full “Saved Passwords Were Found Online” email text is below:
Some of your saved passwords were found online
Some of your saved passwords were found in a data breach from a site or app that you use.Your Account might be affected.
To secure your accounts, Account Password Manager recommends reviewing your passwords now by using below icon
Check passwordsYou can also see security activity at
hxxps://myaccount./notifications
You received this email to let you know about important changes to your Account and services.
Email login credentials are a hot commodity among cybercriminals because email accounts are connected to many other ones. A hijacked email account could result in stolen social media accounts, accessed sensitive accounts, and more. Malicious actors could also use the hijacked accounts to impersonate the owner and ask contacts for money.
How to recognize a phishing email?
Generic phishing attempts that don’t target a specific person tend to be quite obvious. Users should be able to recognize the signs as long as they know what to look for.
One of the first things that users should check when they receive an unsolicited email is the sender’s email address. Low-effort phishing emails will be sent from random-looking email addresses, so they’re an immediate giveaway. More sophisticated emails will use legitimate-looking addresses but with a little research, users should be able to determine whether they are legitimate are not. If users cannot find any evidence that an email address is used by the company the sender claims to be from, they should not trust the email contents.
Another sign of a potential malicious email is grammar/spelling mistakes and awkward phrasing in what’s supposed to be a professional email. This particular “Saved Passwords Were Found Online” email has several mistakes in it, immediately giving it away. The email is also written awkwardly, with several unusual phrases. This email is supposed to look like those automatic ones sent to users to inform them about unusual account activities and such. However, legitimate automatic emails will never have mistakes in them.
Phishing email senders like to create a sense of urgency to pressure users into reacting quickly without double-checking anything. This particular email claims that users’ passwords have been exposed, which will certainly alarm many users and make them react impulsively and try to solve the issue immediately. When dealing with such emails, users should always maintain a clear head and not rush into action. If users inspect the email carefully, they will immediately realize that they don’t use a service called Account Password Manager. There is no password manager using that name at all.
Finally, users should avoid clicking on buttons and links in emails, especially unsolicited ones. If an email asks users to perform some action like secure an account, users should access the account manually instead of using links in the email. In this particular case, if users use a password manager and receive an email saying their password has been leaked, they should open the password manager and check the information there.
Lastly, users should always check a website’s URL before typing in login credentials. Phishing sites can look identical to legitimate sites but the URL will always be different.
Site Disclaimer
WiperSoft.com is not sponsored, affiliated, linked to or owned by malware developers or distributors that are referred to in this article. The article does NOT endorse or promote malicious programs. The intention behind it is to present useful information that will help users to detect and eliminate malware from their computer by using WiperSoft and/or the manual removal guide.
The article should only be used for educational purposes. If you follow the instructions provided in the article, you agree to be bound by this disclaimer. We do not guarantee that the article will aid you in completely removing the malware from your PC. Malicious programs are constantly developing, which is why it is not always easy or possible to clean the computer by using only the manual removal guide.