Mine ransomware removal
Mine ransomware, or .mine file-encrypting malware, will target your personal files and encrypt them. This malware comes from the Djvu/STOP ransomware family, which is controlled by a notorious cybercrime gang that releases new ransomware on a regular basis. The majority of ransomware infections from the Djvu/STOP family are more or less identical to one another, and Mine ransomware is one of the more recent ones. Once it encrypts files, it will demand that you buy a decryptor in order to decrypt them. For users who have no backup, that decryptor may be the only way to recover files. However, buying the decryptor is often a bad idea because it does not always result in the tool being sent.
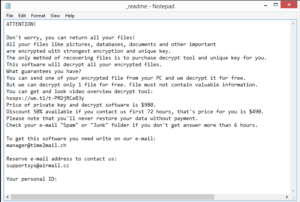
Mine ransomware is mostly identical to Bbnm, Ttii, Hhjk, and Mmob because they all come from the same malware family. These kinds of infections target personal files, usually photos, videos, images, documents, etc. These files are usually the ones users are most willing to pay for, which is why they are targeted. Once encrypted, the files usually have an extension added to them. In this case, the extension .mine is added. For example, text.txt would become text.txt.mine. When all targeted files are done being encrypted, the ransomware will drop _readme.txt ransom notes in all folders that have encrypted files. The notes contain information on how victims can buy decryptors. Unfortunately, for users without backup, that decryptor is currently the only way to recover files. The cybercriminals operating this malware are selling the decryptor for $980 but the note does mention a 50% discount for users who contact them within the first 72 hours. Even with the discount, the decryptor is quite expensive. Furthermore, there are no guarantees that you’ll actually get the decryptor even after paying. You need to consider the fact that you are dealing with cybercriminals. They are the ones who encrypted your files in the first place, it’s doubtful they will feel any kind of obligation to help you. Many users have, unfortunately, not received their decryptors, despite paying. Whether to pay or not is your decision but you should consider the risks.
If you have copies of your files saved in your backup, you can start file recovery as soon as you remove Mine ransomware from your computer. We strongly recommend using anti-malware software for this because ransomware is a very complex malware infection that should be handled by a professional program. If you try to get rid of it manually, you might accidentally cause additional damage to your computer. When your anti-virus program has removed the ransomware, you can safely access your backup.
If you do not have a backup, a free Mine ransomware decryptor may be the only option. However, it’s not yet available, and developing one will be quite difficult for malware researchers. This ransomware uses online keys to encrypt files, which means the keys are unique to each victim. Those keys are needed for a decryptor to work for all victims. But it’s not impossible that a decryptor will eventually be released. While you wait, back up your encrypted files and store them safely. It’s also worth mentioning that there are many fake decryptors advertised on various questionable forums. These fake decryptors could lead to even more malware infections. NoMoreRansom is a safe source for free decryptors.
How did the ransomware enter your computer?
It’s no secret that users with bad online habits are much more likely to infect their computers with malware because they tend to engage in more risky online behavior. If you take the time to develop better online habits, as well as become familiar with malware distribution methods, you should be able to avoid quite a lot of malware in the future.
In case you’re not aware of this, ransomware and other types of malware can often be found in torrents. Many torrent sites are often quite badly regulated, which means malicious actors can easily upload malicious content disguised as torrents for popular movies, TV series, video games, software, etc. The more popular a piece of content is, the more likely its torrent is to contain malware. We strongly recommend you not pirate copyrighted content using torrents because not only is it essentially stealing, but it’s also dangerous for the computer.
But in most cases, users infect their computers with malware when they open unsolicited email attachments that contain malware. This is a very common malware distribution method because it’s somewhat low effort. All malicious actors have to do is buy email addresses from hacker forums, add a malicious file to an email, and send it. The emails are often written to pressure users to open the attachments. For example, the sender may claim to be from some legitimate company emailing an important document that needs to be urgently reviewed. But fortunately, these emails are usually fairly obvious. Despite claiming to be emailing with important business, the senders make many obvious grammar/spelling mistakes in malicious emails. These mistakes make it immediately obvious that an email may be malicious. Another sign of a malicious email is generic words used to address users instead of names. If you receive an email whose attachment you would actually need to open, you would be addressed by your name, not generic words like User, Member, Customer, etc. But it’s worth mentioning that there are more sophisticated malicious spam campaigns, which is why it’s a good idea to scan all email attachments with anti-virus software or VirusTotal before opening them.
How to remove Mine ransomware
Considering that ransomware is a very complex malware infection, it’s not a good idea to try to delete Mine ransomware manually because you could end up causing additional damage to your computer. Furthermore, you might not be able to fully remove Mine ransomware, which could allow it to fully recover later on. If that were to happen while you were accessing your backup, those backed-up files would become encrypted as well. To prevent that from happening, we recommend using reliable anti-malware software. Once the ransomware has been fully removed, you can safely access your backup and start recovering files.
Site Disclaimer
WiperSoft.com is not sponsored, affiliated, linked to or owned by malware developers or distributors that are referred to in this article. The article does NOT endorse or promote malicious programs. The intention behind it is to present useful information that will help users to detect and eliminate malware from their computer by using WiperSoft and/or the manual removal guide.
The article should only be used for educational purposes. If you follow the instructions provided in the article, you agree to be bound by this disclaimer. We do not guarantee that the article will aid you in completely removing the malware from your PC. Malicious programs are constantly developing, which is why it is not always easy or possible to clean the computer by using only the manual removal guide.