About the “Unusual Activities In Your Account” phishing email
“Unusual Activities In Your Account” is a phishing email that tries to steal users’ email account login credentials. The email claims that unusual activities have been noticed in the recipient’s account and the account will be closed if they don’t take action and update their password. If users engage with the email and try to log in to the site the email links to, their login credentials will be stolen.
As far as phishing emails go, this is a pretty generic one. If you receive it, you should be able to identify it as a phishing email. Emails part of this phishing campaign explain that some kind of unusual activities have been noticed on your account. The email asks that you update your information “to avoid your email being disconnected from our server”. Specifically, the email wants you to update your password by clicking on the “Update Password” button. According to the email, unless you update your password, your account will be closed.
The full “Unusual Activities In Your Account” phishing email contents are below:
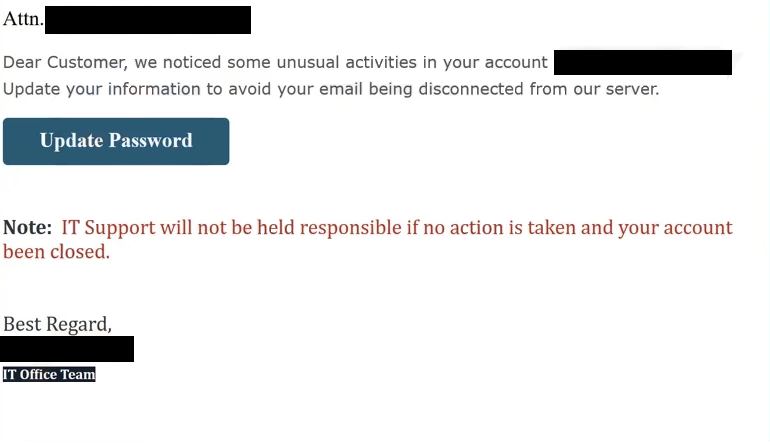
Attn. -,
Dear Customer, we noticed some unusual activities in your account -,
Update your information to avoid your email being disconnected from our server.Update Password
Note: IT Support will not be held responsible if no action is taken and your account been closed.
Best Regard,
–
IT Office Team
If users click on the “Update Password” button, they will be taken to a site that imitates Gmail. The site also displays a pop-up saying your session expired and you need to log in again. If you type in your password, it will be sent to the malicious actors operating this phishing campaign. Cybercriminals could use the credentials themselves or sell them to other malicious actors. Email login credentials are in very high demand among cybercriminals because not only do they contain highly important information but they’re also connected to many other accounts. A successfully hijacked account could allow malicious actors access to countless other
How to recognize phishing emails?
Phishing campaigns that target many users with the same email are usually not difficult to identify because the emails are very generic. They do not contain any credible information and are often full of mistakes. Sophisticated phishing emails are usually reserved for specific targets whose personal information cybercriminals have.
When you receive an unsolicited email asking you to take action (like clicking on a link or opening an attachment), the first thing you should do is check the sender’s email address. You can easily do this by searching the email address on Google to see if it belongs to the person or organization claiming to be the sender. In some cases, malicious email addresses may look random and suspicious, which makes the emails immediately obvious. Some attackers may also use deceptive tactics to make their email addresses appear legitimate, such as using letters like “r” and “n” to imitate “m” or adding extra letters to mimic well-known companies or organizations. For example, they might add an extra “f” to make an address look like it belongs to Netflix.
Another important thing to pay attention to is grammar and spelling mistakes. Phishing emails often contain numerous grammar and spelling errors. While the “Unusual Activities In Your Account” phishing email in question doesn’t have enough text to contain a lot of mistakes, there are still several ones that are easy to notice. You would certainly not see such mistakes in legitimate emails from service providers.
Users should also avoid rushing to take action when they receive such emails, particularly if the email asks users to click on a link or open an email attachment. Instead, they should carefully inspect the email and determine whether it’s plausible for them to receive such an email. For instance, this “Unusual Activities In Your Account” email is clearly fake if you take into account the fact the email providers do not send such emails. They may advise users to change passwords for security reasons but they do not delete accounts because of it.
Finally, when dealing with emails containing links, it is advised not to click on any links at all. If there is an issue with an account that needs attention, users should access the account manually instead of clicking on a link. For instance, if users receive an email from Netflix regarding a failed payment, they should manually access the account and resolve the issue, rather than using the link.
“Unusual Activities In Your Account” phishing email removal
If you receive the “Unusual Activities In Your Account,” email, just delete it. If you have already interacted with the email and entered your email login credentials, it’s important to change your password immediately if your account can still be accessed. It’s also a good idea to review your account activity to check for any unauthorized logins. If your email account has been hijacked, the best course of action is to contact your email service provider to regain control of your account. You also need to disconnect the email address from all other accounts to prevent them from being hijacked as well.
Site Disclaimer
WiperSoft.com is not sponsored, affiliated, linked to or owned by malware developers or distributors that are referred to in this article. The article does NOT endorse or promote malicious programs. The intention behind it is to present useful information that will help users to detect and eliminate malware from their computer by using WiperSoft and/or the manual removal guide.
The article should only be used for educational purposes. If you follow the instructions provided in the article, you agree to be bound by this disclaimer. We do not guarantee that the article will aid you in completely removing the malware from your PC. Malicious programs are constantly developing, which is why it is not always easy or possible to clean the computer by using only the manual removal guide.